ビタミンK2の効果を示すためにはMK-7が必要です
ビタミンK2は、イソプレノイドの鎖長に応じて、長さに応じてMK-4(Menaquinone-4)からMK-13(Menaquinone-13)に分けることができます。
体内に存在し、商業化されたビタミンK2にはMK-4とMK-7があり、バター、チーズなどにはMK-4が含まれ、納豆や韓国料理のチョングクジャンなど豆を発酵した食品にはMK-7が含まれています。
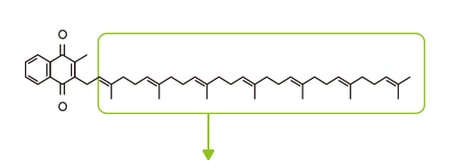
MK-7(K2)
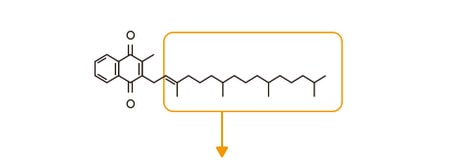
MK-4(K2)
MK-4はほとんど肝臓で代謝され、イソプレノイドの数が少ないため半減期が非常に短く、体内で容易に分解され、摂取量と摂取回数が多くなければ効果が現れません。一方、MK-7の場合、MK-4よりイソプレノイドの数が多く、半減期が3日以上で体内残留時間が長いため、*生体利用率が高いと⾔えます。
つまり、MK-4とMK-7の半減期および摂取量を比較した場合、MK-7摂取時にはMK-4よりも摂取量と摂取回数を減らすことができます。
* 生体利用率: 一定量の薬剤が示す生理的効果
Vitamin K2 concentration in the body (ng/ml)
Time (hour)
The concentration of vitamin K2 in serum (ng/mL) when 420 ㎍ of vitamin K2 is ingested at a time
Vitamin K2 concentration in the body (ng/ml)
The concentration of vitamin K2 in serum (㎍/day) when vitamin K2 60 ㎍ (daily intake) is consumed for 7 consecutive days
Vitamin K (ng/ml)
Accumulation during prolonged intake of MK-4 vs MK-7(60 mcg/day)
Day of suplementation with vitamin K
MK-7とMK-4サプリメントの比較
| 項目 |
MK-7(Menaquinone-7) |
MK-4(Menaquinone-4) |
|---|---|---|
| 推奨量* | 120mcg以上(摂取量が少ない) | 45mg(45,000mcg)(摂取量が多い) |
| 摂取頻度 | 分けて1日3回 | 1日1回 |
| 体内半減期 | 数日(1日1回の摂取が可能) | 数時間(頻繁に摂取が必要) |
*国によって推奨量は異なるが、必要な量よりはるかに少なく設定されている。
